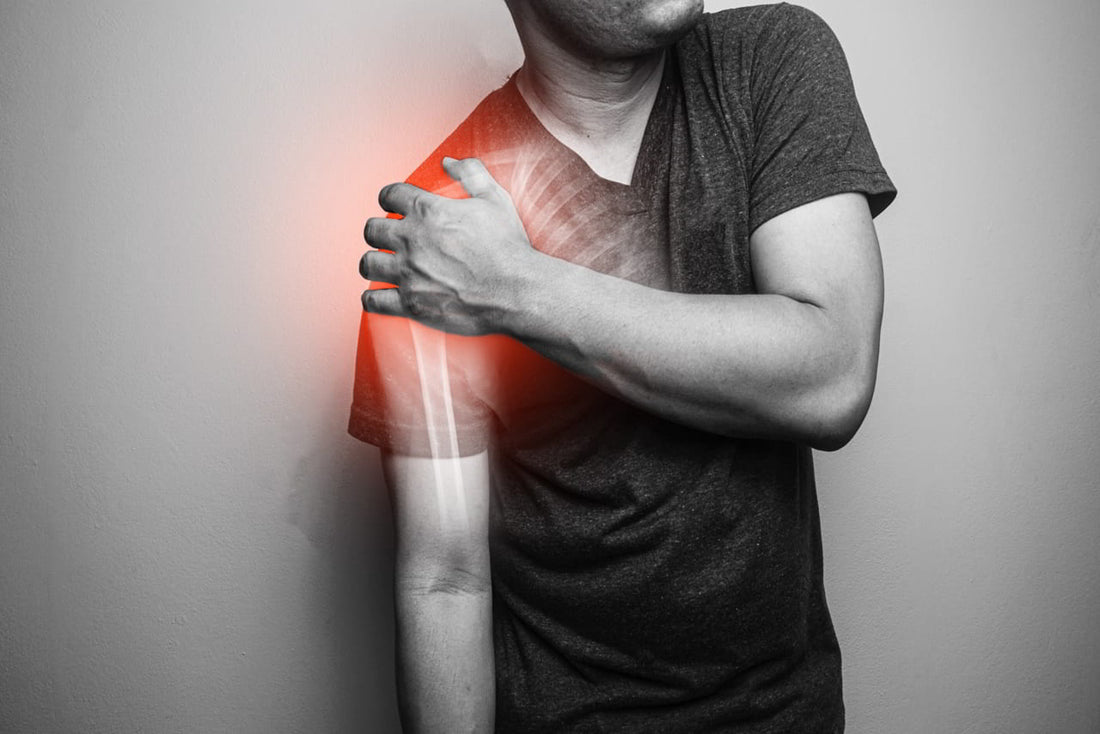
Stress fracture or symptoms of hairline fracture, is one of the most prevalent yet the least bothered bone conditions in the world of orthopedics.
What is Hairline Fracture?
Hairline fracture also known as stress fracture usually develops due to overuse and neglect of bone health and can manifest itself as benign pain in the region of the fracture.
Unlike general fractures that occur due to one-time severe trauma, hairline bone fractures are known to develop over time and are caused due to repeated trauma to the same region. The majority of such fractures occur in weight-bearing bones, including those associated with legs and feet.
symptoms of hairline fracture begin with a fatigued muscle that is no longer able to absorb additional weight or shock. This results in the transference of load onto the bone, which in turn causes minor cracks in the bone structure. The condition is mostly diagnosed among athletes, such as tennis players, runners, and cricketers. Usually, the pain in a hairline fracture is minimal at the start but begins to aggravate as more pressure and shock are borne by the bone.
Though the persisting pain in the case of a stress fracture subsides over time with proper rest, and medication for joint pain, however, if the fracture itself is ignored, then it might lead to more serious bone fractures.
Hairline Fracture Causes
Low bone density stress or hairline fractures can easily be caused by medical conditions that reduce bone density and strength. Illnesses like osteoporosis and the subsequent regimen of long-term medication can lead to hairline fractures even as you carry out day-to-day activities. In the case of sports, according to various studies, women athletes are known to have more symptoms of hairline fracture than male athletes.
This particular pattern is the result of a specific medical condition known as the female athlete triad. What is the female athlete triad? It's a particular condition comprising three interrelated illnesses, namely eating disorders, menstrual dysfunction, and premature osteoporosis, that plague women athletes when they opt for extreme dieting or extreme exercise.
Hairline Bone Fracture Due to Miscalculated Techniques
This particular factor is particularly related to athletes and their training regimens. Most stress fracture-related injuries in athletes occur due to changes in training techniques and mechanics. As the training methods alter, the force and shock absorbed by the bones also experience a drastic change. This often leads to hairline fractures in the leg region if not treated immediately. It also runs the risk of evolving into more aggravated bone injuries.
Supplements for Joint Health, Pain and Inflammation
This specific cause of stress fracture is also most common among athletes and relates primarily to the ones who continuously switch their sporting surfaces and venues. Prevalent among runners and tennis players, the change of surface leads to unbalanced stress on the bones that quickly transform into hairline fractures.
For example, a runner who has switched from a treadmill to a running track is most likely to suffer some form of stress fracture pain and would need constant medical supervision to ensure that the fracture is diagnosed in its earliest stages and treated quickly.
Though stress fractures are easy to detect, courtesy of x-ray, it is always prudent to exercise prevention before cure. It is highly advisable that you maintain a proper diet that is rich in calcium and Vitamin D to ensure that bones remain strong, and also take tablets for joint pain recommended by your doctor. You can start or increase supplements for joint pain to improve bone health.
One such clinically proven food supplement is FlexiQule. Featuring the natural benefits of Ginger and Boswellia, this most effective joint supplement aids in the maintenance of joints and further reduces the risk of bone injuries and symptoms of hairline fracture. Being an anti-inflammatory supplement for joint health and pain relief, FlexiQule significantly decreases cartilage degradation, thereby ensuring the integrity of the bones.
The article is based on the information available in public and which the author believes to be true. The author is not disseminating any information which the author believes or knows is confidential or in conflict with the privacy of any person. The views expressed or information supplied through this article is mere opinion and observation of the author. The author does not intend to defame, insult or cause loss or damage to anyone, in any manner, through this article.